【断酒iOSアプリ制作】飲酒量の視覚化 プログレスバーを作る (5日目)
断酒アプリ制作5日目の本日は、純アルコール量を計算し、飲酒量に応じた色の変化やリスクレベルをわかりやすく表示する「縦型プログレスバー」を作成します。これにより、数値で飲酒量を認識するよりも、ユーザーは自身の飲酒状況を一目で把握できるため、飲み過ぎかどうかの判断がつきやすくなります。
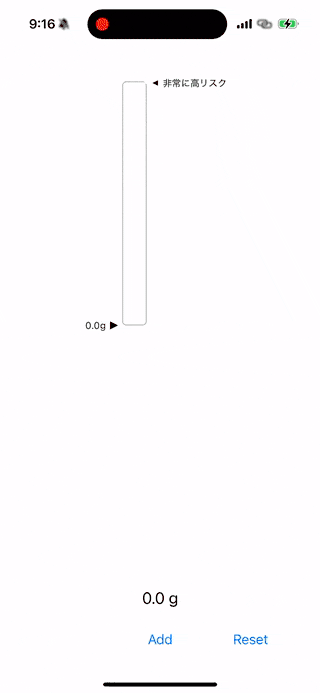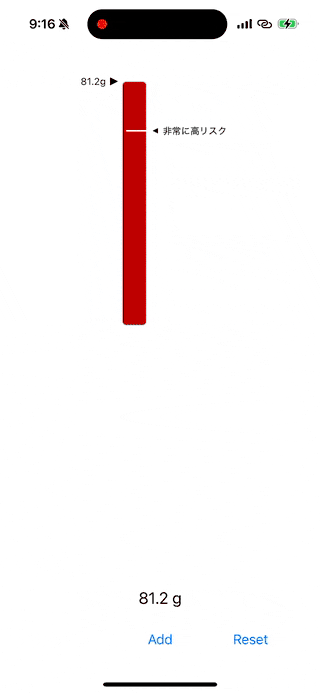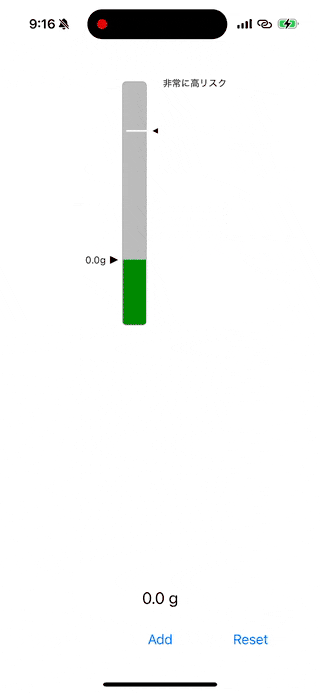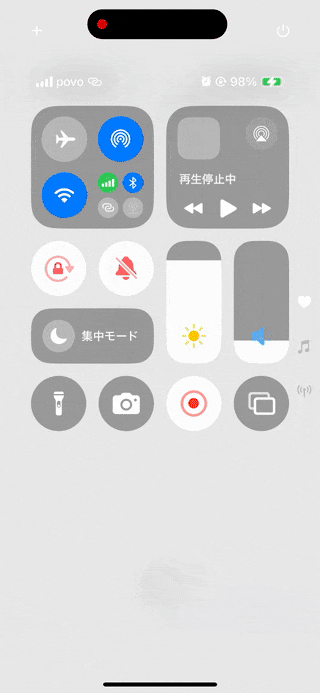
下の動画のような縦型プログレスバーを作ることがゴールになります。
純アルコール量の計算と視覚化
アプリケーションで飲酒量を視覚化するために、純アルコール量を計算し、その危険度をユーザーに示すインターフェースを構築します。本記事では、VerticalProgressBar クラスを作成し、飲酒量を視覚的に表示する方法を解説します。
純アルコール量の計算
純アルコール量を以下の式で計算します。
$$ 純アルコール量 (g) = 飲酒量 (ml) \times アルコール度数 (\%) \times 0.8 $$この値に基づき、飲酒リスクを段階的に分類し、視覚化することで、飲酒量を直感的に理解できるようにします。
危険度の分類
ちなみに純アルコール量に基づく危険度は、以下のように段階的に分類されます。
| 純アルコール量 (g/日) | 危険度の段階 | 健康への影響 |
|---|---|---|
| 0~19g | 低リスク | 健康影響は少ないが、習慣化に注意が必要。 |
| 20~39g | 中リスク | 肝臓疾患や高血圧のリスクがわずかに増加。 |
| 40~59g | 高リスク | アルコール依存症や肝臓疾患のリスク増加。 |
| 60g以上 | 非常に高リスク | アルコール依存症、肝硬変、心血管疾患の危険大。 |
※ 基準は一般的なものです。国や医療機関によって異なる場合があります
注意
- 週単位での評価: 世界保健機関(WHO)や各国のガイドラインでは、週単位での飲酒量の指針を設けています。
- 例: 日本では「男性で1日あたり純アルコール量40g以下、女性で20g以下」が目安とされています。
- 連続飲酒の回避: 少なくとも週2日は休肝日を設けることが推奨されています。
- 個人差: 体重、性別、年齢、体質により影響が異なります。
プログレスバーの実装
VerticalProgressBar クラス
VerticalProgressBar は飲酒量に応じた進捗を縦型プログレスバーで表示するカスタムビューです。
import UIKit
class VerticalProgressBar: UIView {
private let containerView = UIView() // 背景コンテナ
private let progressBar = UIView() // プログレスバー
private let arrowView = UIView() // 三角形の矢印を表示するビュー
private let currentArrowView = UIView() // 現在の状態を示す矢印
var maxAlcoholContent: Double = 60.0 // 最大値を設定
var maxAlcoholContentTitle: String = "非常に高リスク" // 最大値のタイトル
private var internalProgress: Double = 0.0 // プログレスバーの進捗状況
var progress: Double {
get {
internalProgress
}
set {
internalProgress = newValue
updateProgress()
}
}
override init(frame: CGRect) {
super.init(frame: frame)
setupViews()
}
required init?(coder: NSCoder) {
super.init(coder: coder)
setupViews()
}
private func setupViews() {
// 背景コンテナ
containerView.layer.borderWidth = 1
containerView.layer.borderColor = UIColor.lightGray.cgColor
containerView.clipsToBounds = true
containerView.layer.cornerRadius = 5 // 背景のみ角丸にする
addSubview(containerView)
// プログレスバー
progressBar.backgroundColor = .green
containerView.addSubview(progressBar)
// 最大値を示す矢印を作成
arrowView.backgroundColor = .clear
addSubview(arrowView)
// 現在の状態を示す矢印を作成
currentArrowView.backgroundColor = .clear
addSubview(currentArrowView)
}
// レイアウトの更新
override func layoutSubviews() {
super.layoutSubviews()
containerView.frame = bounds
updateProgress()
}
// プログレスバーの更新
private func updateProgress() {
let containerHeight = containerView.bounds.height
// プログレスバーの高さを計算
let progressHeight = CGFloat(min(internalProgress / maxAlcoholContent, 1.0)) * containerHeight
// アニメーションでプログレスバーの増加をスムーズに
UIView.animate(withDuration: 0.3, animations: {
self.progressBar.frame = CGRect(
x: 0,
y: containerHeight - progressHeight,
width: self.containerView.bounds.width,
height: progressHeight
)
})
// 矢印の位置を更新
let arrowPosition: CGFloat
if internalProgress > maxAlcoholContent {
arrowPosition = CGFloat((maxAlcoholContent / internalProgress) * containerHeight)
} else {
arrowPosition = CGFloat(containerHeight)
}
updateArrow(position: arrowPosition)
updateCurrentArrow(position: containerHeight - progressHeight)
// 色のアニメーションを追加
animateColorChange(for: progressBar, to: calculateColor(for: internalProgress))
}
// 色のアニメーション
private func animateColorChange(for view: UIView, to color: UIColor) {
UIView.transition(with: view, duration: 0.3, options: [.transitionCrossDissolve], animations: {
view.backgroundColor = color
})
}
// 進捗に応じた色を計算
private func calculateColor(for progress: Double) -> UIColor {
// 色の範囲(緑→黄色→赤→黒)
let green = UIColor.green
let yellow = UIColor.yellow
let red = UIColor.red
let black = UIColor.black
if progress <= maxAlcoholContent {
// 緑→黄色→赤の間
let normalizedProgress = progress / maxAlcoholContent
if normalizedProgress < 0.5 {
return interpolateColor(from: green, to: yellow, fraction: CGFloat(normalizedProgress * 2.0))
} else {
return interpolateColor(from: yellow, to: red, fraction: CGFloat((normalizedProgress - 0.5) * 2.0))
}
} else {
// 赤→黒の間
let overLimitProgress = (progress - maxAlcoholContent) / maxAlcoholContent
return interpolateColor(from: red, to: black, fraction: CGFloat(min(overLimitProgress, 1.0)))
}
}
// 色の補間
private func interpolateColor(from: UIColor, to: UIColor, fraction: CGFloat) -> UIColor {
// UIColorのコンポーネントを取得
var fromRed: CGFloat = 0, fromGreen: CGFloat = 0, fromBlue: CGFloat = 0, fromAlpha: CGFloat = 0
var toRed: CGFloat = 0, toGreen: CGFloat = 0, toBlue: CGFloat = 0, toAlpha: CGFloat = 0
from.getRed(&fromRed, green: &fromGreen, blue: &fromBlue, alpha: &fromAlpha)
to.getRed(&toRed, green: &toGreen, blue: &toBlue, alpha: &toAlpha)
// 線形補間で色を計算
let red = fromRed + (toRed - fromRed) * fraction
let green = fromGreen + (toGreen - fromGreen) * fraction
let blue = fromBlue + (toBlue - fromBlue) * fraction
let alpha = fromAlpha + (toAlpha - fromAlpha) * fraction
return UIColor(red: red, green: green, blue: blue, alpha: alpha)
}
// 矢印の位置を更新
private func updateArrow(position: CGFloat) {
let arrowWidth: CGFloat = 10
let arrowHeight: CGFloat = 10
let horizontalBarWidth: CGFloat = containerView.bounds.width // 水平棒の幅
// 三角形と水平棒を一つのパスで描画
let path = UIBezierPath()
// 三角形の描画(右側)
path.move(to: CGPoint(x: arrowWidth, y: 0))
path.addLine(to: CGPoint(x: 0, y: arrowHeight / 2))
path.addLine(to: CGPoint(x: arrowWidth, y: arrowHeight))
path.close()
// 水平棒の描画
path.move(to: CGPoint(x: -horizontalBarWidth, y: arrowHeight / 2)) // 棒の始点
path.addLine(to: CGPoint(x: 0, y: arrowHeight / 2)) // 棒の終点
let shapeLayer = CAShapeLayer()
shapeLayer.path = path.cgPath
shapeLayer.fillColor = UIColor.black.cgColor
shapeLayer.strokeColor = UIColor.white.cgColor // 水平棒の色
shapeLayer.lineWidth = 2.0 // 水平棒の太さ
arrowView.layer.sublayers?.forEach { $0.removeFromSuperlayer() } // 既存の三角形を削除
arrowView.layer.addSublayer(shapeLayer)
// アニメーションで矢印の移動をスムーズに
UIView.animate(withDuration: 0.3, animations: {
self.arrowView.frame = CGRect(
x: self.containerView.frame.maxX + 5,
y: self.bounds.height - position - (arrowHeight / 2) + 2,
width: arrowWidth,
height: arrowHeight
)
})
// ラベルを追加または更新
if let label = viewWithTag(9001) as? UILabel {
UIView.animate(withDuration: 0.3, animations: {
label.frame = CGRect(
x: self.arrowView.frame.maxX + 5,
y: self.arrowView.frame.midY - 10,
width: 80,
height: 20
)
})
} else {
let label = UILabel()
label.text = maxAlcoholContentTitle
label.font = UIFont.systemFont(ofSize: 12)
label.textColor = .black
label.tag = 9001 // ラベルをタグで管理
label.frame = CGRect(
x: arrowView.frame.maxX + 5,
y: arrowView.frame.midY - 10,
width: 80,
height: 20
)
addSubview(label)
}
}
// 現在の状態を示す矢印の位置を更新
private func updateCurrentArrow(position: CGFloat) {
let arrowWidth: CGFloat = 10
let arrowHeight: CGFloat = 10
// 矢印を三角形に描画(現在の状態を示す矢印)
let path = UIBezierPath()
path.move(to: CGPoint(x: 0, y: 0))
path.addLine(to: CGPoint(x: arrowWidth, y: arrowHeight / 2))
path.addLine(to: CGPoint(x: 0, y: arrowHeight))
path.close()
let shapeLayer = CAShapeLayer()
shapeLayer.path = path.cgPath
shapeLayer.fillColor = UIColor.black.cgColor
currentArrowView.layer.sublayers?.forEach { $0.removeFromSuperlayer() } // 既存の三角形を削除
currentArrowView.layer.addSublayer(shapeLayer)
// アニメーションで矢印の移動をスムーズに
UIView.animate(withDuration: 0.3, animations: {
self.currentArrowView.frame = CGRect(
x: self.containerView.frame.minX - 15,
y: position - 5,
width: arrowWidth,
height: arrowHeight
)
})
// ラベルを追加または更新
if let label = viewWithTag(9002) as? UILabel {
// ラベルの値を更新
label.text = String(format: "%.1fg", internalProgress)
UIView.animate(withDuration: 0.3, animations: {
label.frame = CGRect(
x: self.currentArrowView.frame.minX - 55, // 三角形の左側に配置
y: self.currentArrowView.frame.midY - 10,
width: 50,
height: 20
)
})
} else {
let label = UILabel()
label.text = String(format: "%.1fg", internalProgress)
label.font = UIFont.systemFont(ofSize: 12)
label.textColor = .black
label.textAlignment = .right
label.tag = 9002 // ラベルをタグで管理
label.frame = CGRect(
x: currentArrowView.frame.minX - 55, // 三角形の左側に配置
y: currentArrowView.frame.midY - 10,
width: 50,
height: 20
)
addSubview(label)
}
}
// 水平線を描画
private func drawHorizontalLine(at yPosition: CGFloat) {
// 既存の水平線を削除
containerView.layer.sublayers?.removeAll(where: { $0.name == "HorizontalLine" })
// 水平線を描画
let linePath = UIBezierPath()
linePath.move(to: CGPoint(x: 0, y: yPosition))
linePath.addLine(to: CGPoint(x: containerView.bounds.width, y: yPosition))
let lineLayer = CAShapeLayer()
lineLayer.path = linePath.cgPath
lineLayer.strokeColor = UIColor.white.cgColor // 水平線を白色に設定
lineLayer.lineWidth = 2.0 // 線の太さを調整
lineLayer.shadowColor = UIColor.black.cgColor // 影を追加して視認性を向上
lineLayer.shadowOpacity = 0.8
lineLayer.shadowRadius = 1
lineLayer.shadowOffset = CGSize(width: 0, height: 1)
lineLayer.name = "HorizontalLine" // 識別のため名前を付ける
containerView.layer.addSublayer(lineLayer)
}
// リセット機能
func reset() {
internalProgress = 0.0
updateProgress()
// ラベルを削除
if let label = viewWithTag(9001) as? UILabel {
label.removeFromSuperview()
}
}
}
主なプロパティと機能
- progress: 現在の純アルコール量を設定します。
- maxAlcoholContent: プログレスバーの最大値(例:60g)。
- updateProgress(): プログレスバーを更新し、進捗に応じた色や矢印を表示します。
カラーの変化
calculateColor(for:) メソッドでは、飲酒量に応じて以下のように色を変化させます:
- 緑 → 黄色 → 赤:低リスクから高リスクへ。
- 赤 → 黒:高リスクを超えた場合。
現在の飲酒量とリスクレベルの表示
updateArrow(position:) と updateCurrentArrow(position:) メソッドで、現在のリスクレベルや飲酒量を矢印とラベルで表示します。
コードの使い方
プログレスバーの配置
VerticalProgressBar を画面に追加し、飲酒量をリアルタイムで更新します。
import UIKit
class ViewController: UIViewController {
@IBOutlet weak var totalLabel: UILabel!
private var totalPureAlcoholContent: Double = 0.0
private let progressBar = VerticalProgressBar()
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
// プログレスバーをプログラムで追加
progressBar.frame = CGRect(x: 150, y: 100, width: 30, height: 300)
progressBar.maxAlcoholContent = 60.0 // 最大値を設定
view.addSubview(progressBar)
...
}
ボタンによる進捗の更新
ボタンを押すたびにランダムなアルコール量を追加し、プログレスバーとラベルを更新します。
@IBAction func onTappedClick(_ sender: Any) {
let randomAlcohol = Double.random(in: 2.0...10.0)
totalPureAlcoholContent += randomAlcohol
progressBar.progress = totalPureAlcoholContent
totalLabel.text = String(format: "%.1f g", totalPureAlcoholContent)
}リセット機能
飲酒量とプログレスバーをリセットします。
@IBAction func onTappedReset(_ sender: UIButton) {
totalPureAlcoholContent = 0.0
progressBar.reset()
totalLabel.text = String(format: "%.1f g", totalPureAlcoholContent)
}サンプルアプリ
GitHubリポジトリでサンプルコードを公開しています:
リポジトリ内の AlcoholMeterSampleApp ターゲットをビルドすると動作を確認できます。
まとめ
純アルコール量を計算し、飲酒量を視覚的に表示することでユーザーに危険度を知らせる仕組みを構築。
- VerticalProgressBar を使い、リアルタイムのデータ反映が可能。
- 飲酒量とリスクを色や矢印で直感的に伝えるUIを実現。
この記事を参考に、あなた自身のアプリ開発にも取り入れてみてください。